There are many reasons for formation subsidence, including natural and man-made factors. Some of the main factors of influence are summarized as follows:
Causes of natural subsidence
Formation compaction: The near surface of the modern alluvial layer will be caused by the impact of gravity and pressure, resulting in rapid settlement of the ground height. Such effects often occur in coastal plains and estuarine deltas, such as the Mississippi R. Delta region.
Sea level rise: global sea level rise also causes relative subsidence. This phenomenon is common in coastal plains.
Geological tectonic activity: continuous and slow crustal elastic/inelastic deformation, and instantaneous crustal movement will cause vertical deformation of the formation, resulting in subsidence or uplift of the regional strata. Such movements are common in the subduction islands.
Natural surface pressure Changes: Seasonal changes in surface water volume, and snow changes can lead to seasonal vertical height changes. Such changes can result in vertical elevation changes in the public hierarchy.
crustal elastic deformation: Influenced by the distribution of continental glaciers and oceans, the continental crust produces varying degrees of bending deformation, resulting in vertical height changes in different areas of the Earth's crust.
Volcanic activity: Volcanic activity and corresponding magma flow may also produce the formation subsidence in the upper region.
Causes of artificial subsidence
Groundwater loss: Excessive extraction of groundwater, or groundwater recharge is less than the amount of artificial extraction will accelerate formation compaction effect and lead to formation subsidence.
Extra weight of artificial buildings: building large buildings on an airtight sedimentary stratum creates additional pressure on the stratum, resulting in subsidence.
Underground resources mining: natural gas, oil and other open practice will also lead to the surface subsidence above the mining area.
According to the report of the Water Conservancy Department of the Ministry of Economy's subsidence level, there are still Zhanghua County, Yunlin County and Pingdong County in the area of the notable subsidence in the Taiwan area until 103. Among them, the Zhanghua County continued subsidence area occurred in Xihu Town and Xizhou two townships, an area of about 1.5 square kilometers. Yunlin County Persistent subsidence areas are Hu Yu, Toucoux, Yuanchang, Baozhong, Lun back township, Taixi, Shihu and Shu Lin, and other eight townships, an area of about 307.6 square kilometers. Other places, such as the Pingdong, are also a region with a severe subsidence, and there are varying degrees of subsidence in the Yilan, Taipei Basin, in the northeastern part of the city.
Different types of subsidence

Image source: Wikipedia
.jpg?crc=4152602394)
Image source: Wikipedia
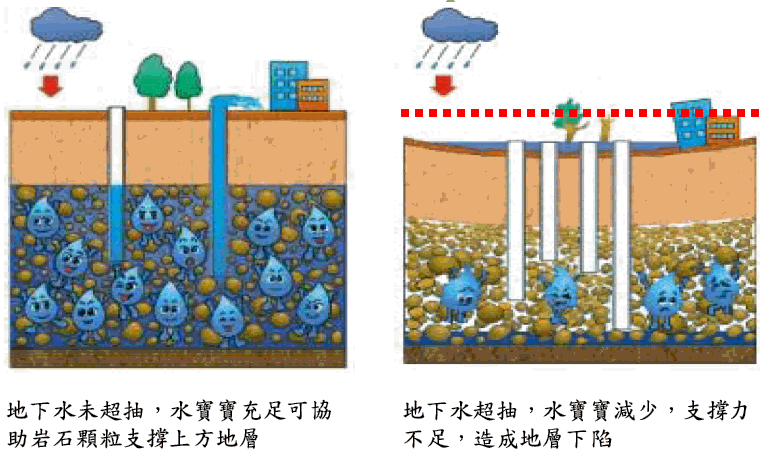
Source: Formation subsidence Control Service Regiment

Image source: Trap Direct hit-Public news

Image source: Classic Magazine
Data source: YouTube
Data source: YouTube
Data source: YouTube




